Common Symptoms of Heart Attack
Understanding the warning signs of a heart attack can help you seek immediate medical attention and potentially save your life.
What are the Common Symptoms of a Heart Attack?
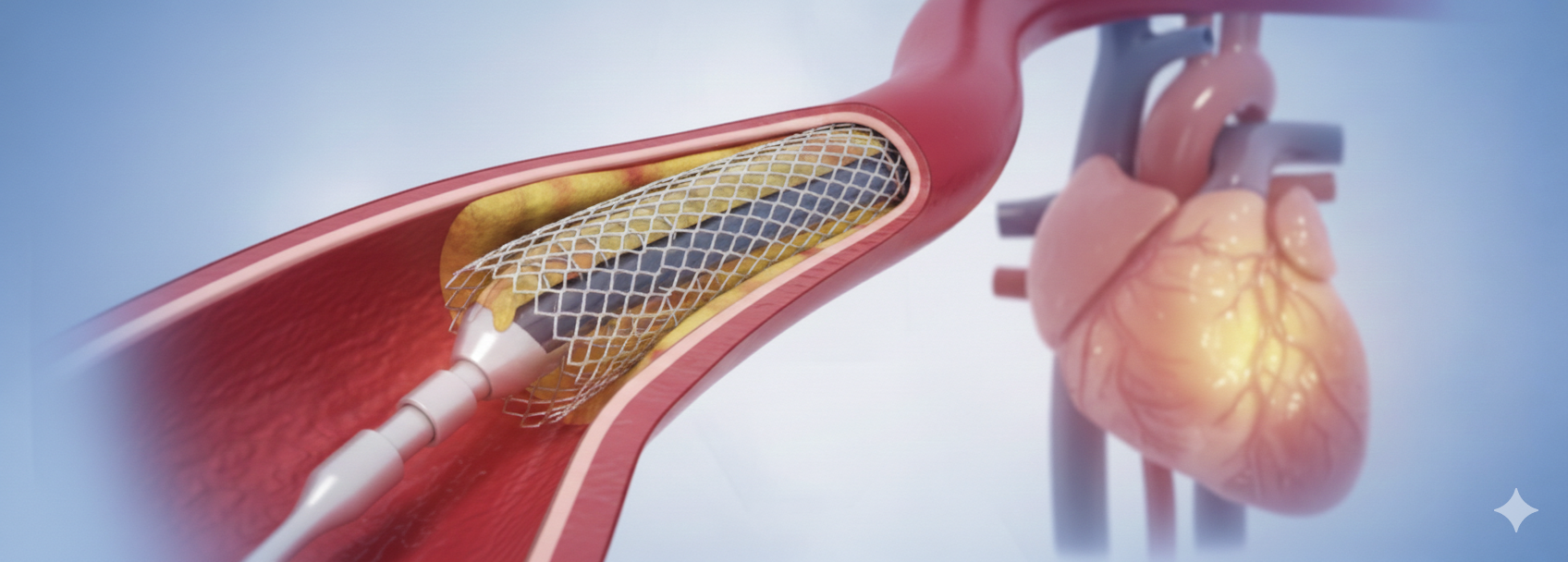
Common symptoms of a heart attack include chest pain or discomfort, pain or discomfort in one or both arms, jaw, neck, back, or stomach, shortness of breath, sweating, nausea, and lightheadedness. These symptoms can vary between individuals, and some people may experience a "silent" heart attack with few or no noticeable symptoms.
Chest Pain or Discomfort: This is the most common symptom and can feel like pressure, squeezing, fullness, or pain in the center of the chest. It may last for more than a few minutes, or it may come and go.
Pain or Discomfort in Other Areas: Pain or discomfort can radiate to one or both arms, the back, neck, jaw, or stomach.
Shortness of Breath: This may occur with or without chest discomfort and can be a sign of reduced blood flow to the heart.
Sweating: Sudden, excessive sweating, especially with cold, clammy skin, can be a sign.
Nausea and Vomiting: Feeling sick to the stomach or throwing up can also occur.
Lightheadedness or Dizziness: Feeling faint or having a sudden loss of balance can be a warning sign.
Fatigue: Feeling unusually tired or weak, especially in women, can be a symptom.
Anxiety: Some individuals may experience a sense of impending doom or anxiety.
Preventive Measures for Heart Attack :
Quit Smoking :
Smoking : Significantly increases the risk of heart disease.
Quitting : Reduces the risk of heart attack within 24 hours of quitting and reduces the risk of heart disease to half that of a smoker within a year.
Limit Alcohol : No level of alcohol consumption is safe for health.
Stress Management :
Stress : Can contribute to unhealthy habits like overeating and lack of exercise.
Stress-reducing techniques : Yoga, meditation, deep breathing exercises, and hobbies.
Sleep :
Aim for: 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night.
Tips : Create a bedtime routine, keep electronic devices out of the bedroom, and be physically active during the day.
2. MEDICAL MANAGEMENT:
Monitor : Blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and diabetes.
Consult a cardiologist : If there's a family history of heart disease.
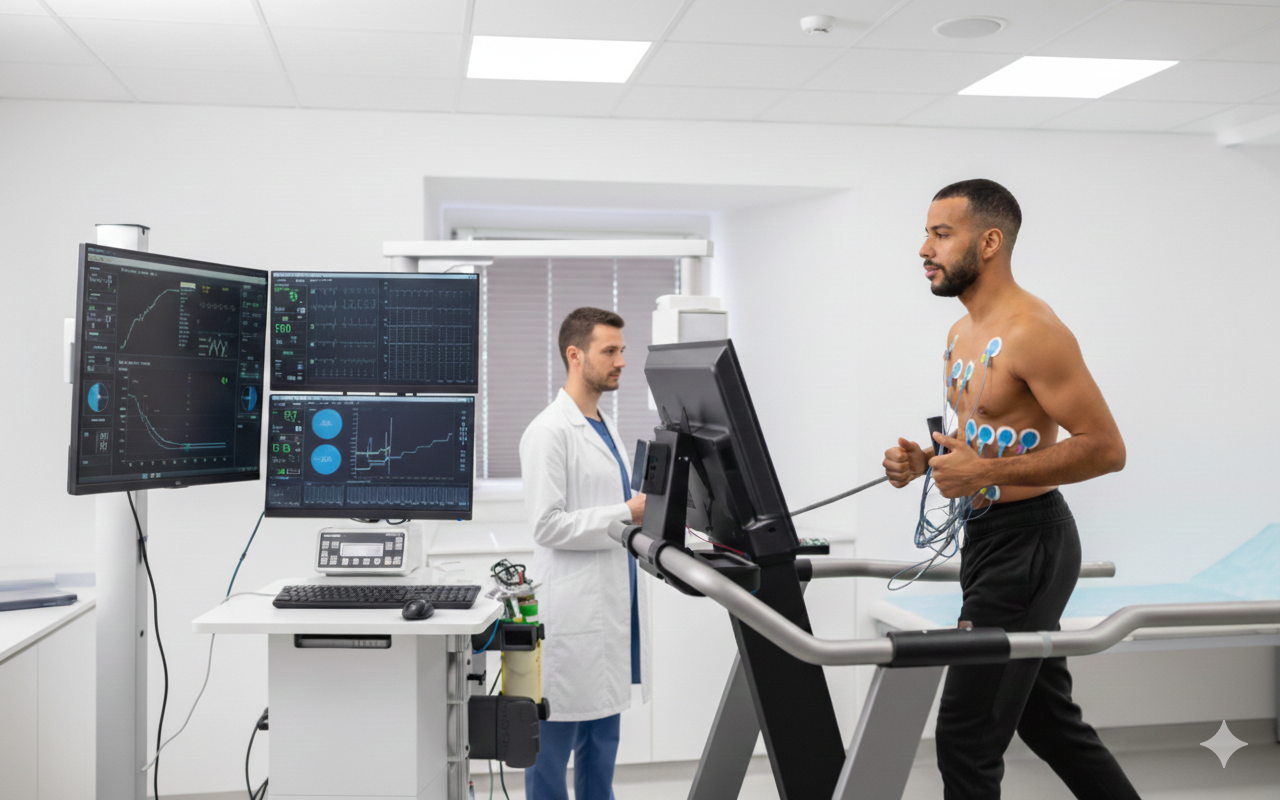
Regular Checkup : Prophylactic Tests like ECG, ECHO, Stress Test may help to detect disease early.
Follow :
Doctor's advice on medications for managing blood pressure, cholesterol, diabetes, etc.